Agile Interview Questions
Q #1) What is Agile Testing?
Answer: Agile Testing is a
practice that a QA follows in a dynamic environment where testing requirements
keep changing according to customer needs. It is done parallel to the
development activity where the testing team receives frequent small codes from
the development team for testing.
Q #2) What is the difference
between burn-up and burn-down charts?
Answer: Burn-up and burn-down
charts are used to keep track of the progress of the project.
Burn-up charts represent how
much work has been completed in any project whereas Burn-down chart represents
the remaining work in a project.
Q #3) Define the roles in Scrum?
Answer:
There are mainly three roles
that a Scrum team have:
1. Project Owner has
the responsibility of managing the product backlog. Works with end-users and
customers and provides proper requirements to the team to build the proper
product.
2. Scrum Master works with
the scrum team to make sure each sprint gets completed on time. Scrum master ensures proper workflow for the
team.
3. Scrum Team: Each
member of the team should be self-organized, dedicated and responsible for the
high quality of the work.
Q #4) What is Product Backlog
& Sprint Backlog?
Answer: The Product backlog is maintained by the project owner
which contains every feature and requirement of the product.
Sprint backlog can be treated as the
subset of product backlog which contains features and requirements related to
that particular sprint only.
Q #5) Explain Velocity in
Agile.
Answer: Velocity is a metric
that is calculated by the addition of all efforts estimates associated with
user stories completed in an iteration. It predicts how much work Agile can
complete in a sprint and how much time will it require to complete a project.
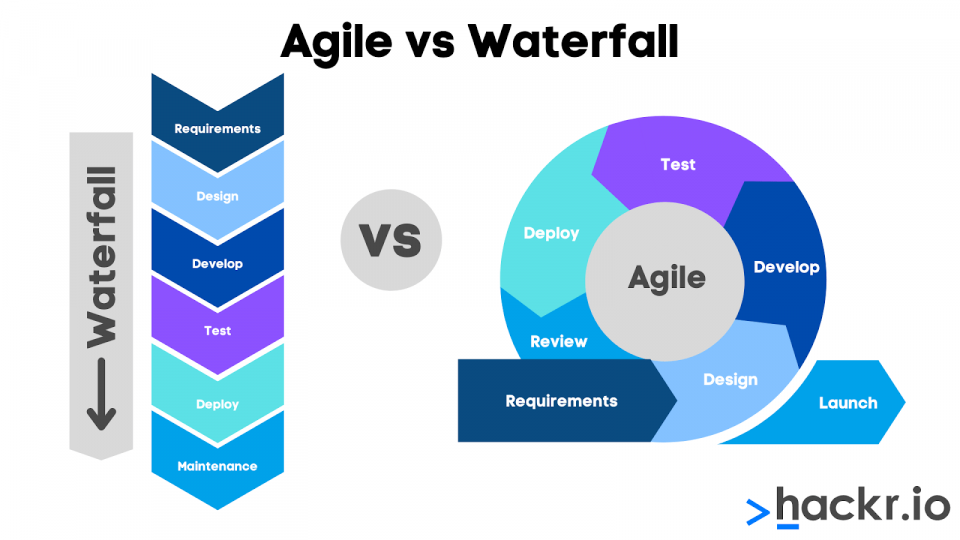
Q #6) Explain the difference
between a traditional Waterfall model and Agile
testing?
Answer: Agile testing is done
parallel to the development activity whereas a traditional waterfall model
testing is done at the end of the development.
As done in parallel, agile
testing is done on small features whereas, in a waterfall model, testing is
performed on the whole application.
Q
#7) Explain Pair Programming and its benefits?
Answer: Pair programming is a
technique in which two programmer works as a team in which one programmer
writes code and other one reviews that code. They both can switch their roles.
Benefits:
·
Improved code quality: As the second partner reviews
the code simultaneously, it reduces the chances of mistake.
·
Knowledge transfer is easy: One experienced partner can
teach another partner about the techniques and codes.
Q #8) What is Re-factoring?
Answer: Modification of the
code without changing its functionality to improve the performance is called
Re-factoring.
Q #9) Explain the Iterative and
Incremental Development in Agile?
Answer:
Iterative Development: Software is developed and
delivered to the customer and based on the feedback again developed in cycles
or releases and sprints. Example: Release
1 software is developed in 5 sprints and delivered to the customer. Now, the
customer wants some changes, then the development team plan for 2nd release which can be completed in some sprints and
so on.
Incremental Development: Software is developed in
parts or increments. In each increment, a portion of the complete requirement
is delivered.
Q #10) How do you deal when
requirements change frequently?
Answer: This question is to
test the analytical capability of the candidate.
The answer can be: Work
with PO to understand the exact requirement to update test cases. Also,
understand the risk of changing the requirement. Apart from this, one should be
able to write a generic test plan and test cases. Don’t go for the automation
until requirements are finalized.
Q #11) What is a test stub?
Answer: Test stub is a small code
that mimics a specific component in the system and can replace it. Its output
is the same as the component it replaces.
Q #12) What qualities should a
good Agile tester have?
Answer:
·
He should be able to understand the requirements quickly.
·
He should know Agile concepts and principals.
·
As requirements keep changing, he should understand the risk
involved in it.
·
The agile tester should be able to prioritize the work based on
the requirements.
·
Communication is a must for an Agile tester as it requires a lot
of communication with developers and business associates.
Q #13) What is the difference
between Epic, User stories & Tasks?
Answer:
User Stories: It defines the actual
business requirement. Generally created by the business owner.
Task: To accomplish the business requirements
development team create tasks.
Epic: A group of related user stories is called an
Epic.
Q #14) What is a Taskboard in
Agile?
Answer: Taskboard is a
dashboard that shows the progress of the project.
It contains:
·
User Story: It has the actual business requirement.
·
To Do: Tasks that can be worked on.
·
In Progress: Tasks in progress.
·
To Verify: Tasks pending for verification or testing
·
Done: Completed tasks.
Q #15) What is Test Driven
Development (TDD)?
Answer: It is a Test-first
development technique in which we add a test first before we write the complete
production code. Next, we run the test and based on the result refactor the code
to fulfill the test requirement.
Q #16) How QA can add value to
an agile team?
Answer: QA can provide value
addition by think outside the box about the various scenarios to test a story.
They can provide quick feedback to the developers about whether new
functionality is working fine or not.
Q #17) What is Scrum ban?
Answer: It is a software
development model that is a combination of Scrum and Kanban. Scrumban is
considered for maintaining projects in which there are frequent changes or
unexpected user stories. It can reduce the minimum completion time for user
stories.
Q #18) What is the Application
Binary Interface?
Answer: Application Binary
Interface or ABI is defined as an interface for complied application programs
or we can say it describes the low-level interface between an application and
the operating system.
Q #19) What is the Zero sprint
in Agile?
Answer: It can be defined as a
pre-preparation step to the first sprint. Activities like setting development
environment, preparing backlog, etc need to be done before starting the first
sprint and can be treated as Sprint zero.
Q #20) What is Spike?
Answer: There may be some
technical issues or design problem in the project which needs to be resolved
first. To provide the solution to this problem “Spikes” are created.
Spikes are of two types- Functional and
Technical.
Q #21) Name some Agile quality
strategies.
Answer: Some Agile quality strategies are-
1. Re-factoring
2. Small
feedback cycles
3. Dynamic code
analysis
4. Iteration
Q #22) What is the importance
of daily stand up meetings?
Answer: Daily stand up meeting
is essential for any team in which team discuss,
1. How much
work has been completed?
2. What are the
plans to resolve technical issues?
3. What steps
need to done to complete the projects etc?
Q #23) What is a tracer bullet?
Answer: It can be defined as a spike
with the current architecture or the current set of best practices. The
purpose of a tracer bullet is to examine how an end-to-end process will work
and examine feasibility.
Q #24) How the velocity of the
sprint is measured?
Answer: If capacity is measured
as a percentage of a 40 hours weeks then, completed story points * team
capacity
If capacity is measured in
man-hours then Completed story points/team capacity
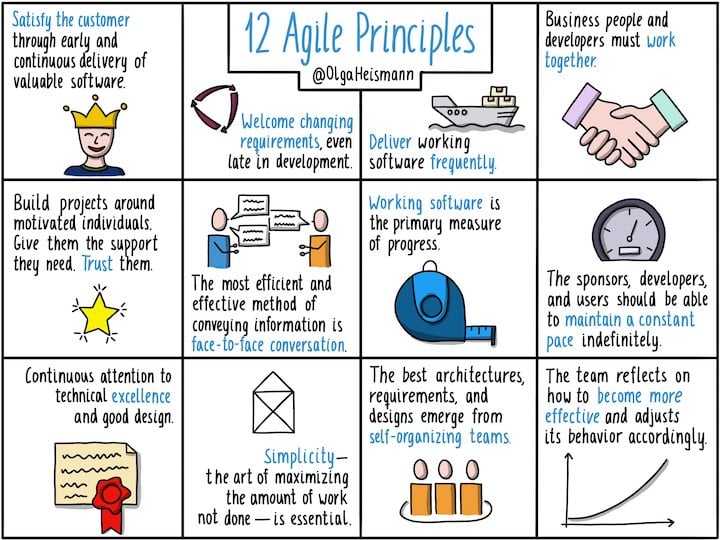
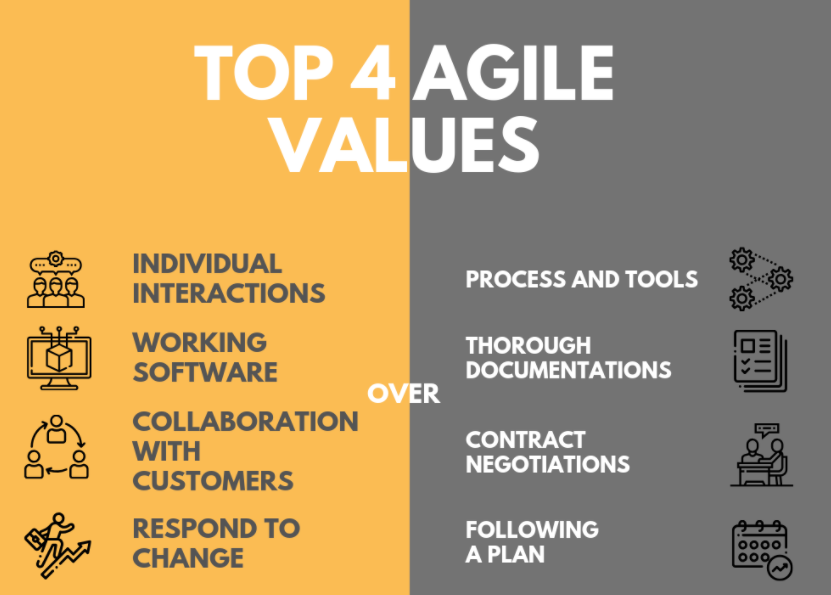
Q #25) What is Agile manifesto?
Answer: Agile manifesto defines
an iterative and people-centric approach to software development. It has 4 key
values and 12 principals.
4 key values
- Individuals and
interactions over processes and tools.
- Working software over
comprehensive documentation.
- Customer
collaboration over contract negotiation.
- Responding to change
over following a plan.
12 Principles
- Satisfy the Customer
Through Early and Continuous Delivery of Valuable Software
- Welcome Changing
Requirements, Even Late in Development
- Deliver Working
Software Frequently
- Business People and
Developers Must Work Together
- Build Projects Around
Motivated Individuals
- Promote Face-to-Face
Conversations
- Working Software Is
the Primary Measure of Progress
- Agile Processes
Promote Sustainable Development
- Continuous Attention
to Technical Excellence and Good Design Enhances Agility
- Simplicity—the Art of
Maximizing the Amount of Work Not Being Done—is Essential
- The Best
Architectures, Requirements and Designs Emerge from Self-organizing
Teams
- Have Regular
Intervals
Q
#26) Is there any disadvantage of the agile model (SDLC)?
Answer: Disadvantages of Agile
SDLC:
- The development team
should be highly professional and client-oriented.
- New requirement may
be a conflict with the existing architecture.
- With further
correction and change, there may be chances that the project will cross
the expected time.
- There may be
difficult to estimate the final coast of the project due to constant
iteration.
- A defined requirement
is absent.
Q
#27) What do you understand about Scrum?
Answer: Scrum is a
framework that helps agile teams work together to develop, deliver, and sustain
the complex product in the shortest time. The product provides by scrum team in
this shortest period is known as a sprint.
Q #28) What are the
responsibilities of the Scrum Master?
Answer: The critical
responsibility of Scrum Master includes:
- Tracking and
monitoring project development.
- Understanding the
user requirement correctly.
- Work to obtain the
project properly.
- Improving the
performance of the team.
- Organized meetings
and resolve issues.
- Communicate and
report to the customer and development team.
Q
#29) What are different ceremonies and their importance in Scrum?
Answer: To clearly express
the
- Scrum planning,
- Scrum review,
- Scrum Daily stand up,
and
- scrum
retrospective
is the purpose of
the ceremony. The importance of these ceremonies is to use sprint as per your
project.
Q #30) What are the major
principles of agile testing?
Answer: Some of the essential
principles of agile testing are:
- Customer
satisfaction
- Face to face
communication
- Sustainable
development
- Continuous feedback
- Quick respond to
changes
- Successive
improvement
- Self-organized
- Focus on
essence
- Error-free clean
node
- Collective work
No comments:
Post a Comment