1. What is Docker?
· Docker is an
open platform that provides the capability to develop, test, ship and
run your application in an isolated environment. This isolated environment is
called container. Containers are light weighted as they directly run
within the host machine's kernel.
· Docker
enables you to keep your application separate from your Infrastructure and it
reduces the delay between developing your application and deploying it in
production.
· Docker runs
the applications in isolation with security, it allows you to run many
containers on a host machine.
2. What is the Docker Engine?
Docker
Engine is an application which has client-server type
architecture with these major components.
- Daemon Process
('dockerd' command) - It's a server which is a type of long running program.
- A Rest API - It
provides an interface that programs or CLI use to talk to daemon processes
and to instruct it.
- A CLI (Command Line
Interface) client ('docker' command).
Source: Docker Overview
3. What can you use Docker for?
You can use the docker for:
- Fast and consistent
delivery of applications- means dockers allows developers to streamline
their work by allowing them to work on local containers which provide
their applications and services. Containers are best suited for CI
(Continuous Integration) and CD (Continuous Delivery)
- Scaling and
Responsive deployment - means docker's container based platform allows for
highly portable workloads and docker containers can run on developers
laptop, on physical or virtual machines, on cloud provider or in a hybrid
environment.
- Running more
workloads on the same hardware - means docker provides a cost effective
alternative of hypervisor based virtual machines so that you can consume
more compute capacity without changing the existing hardware. Docker is
very lightweight and fast.
4. Give some
Docker Example scenarios.
As Docker provides the
consistent and fast delivery of applications, these are the below examples for
that.
- Developers write the
code and can share that with their team members using dockers containers.
- Docker is used to
push the code and execute automated or manual tests in a Test environment.
- Developers can fix
the bugs in the development environment and can push them to the test
environment for testing.
- Giving fixes or
updated applications to customers is easy as you can push the updated
image to the Production.
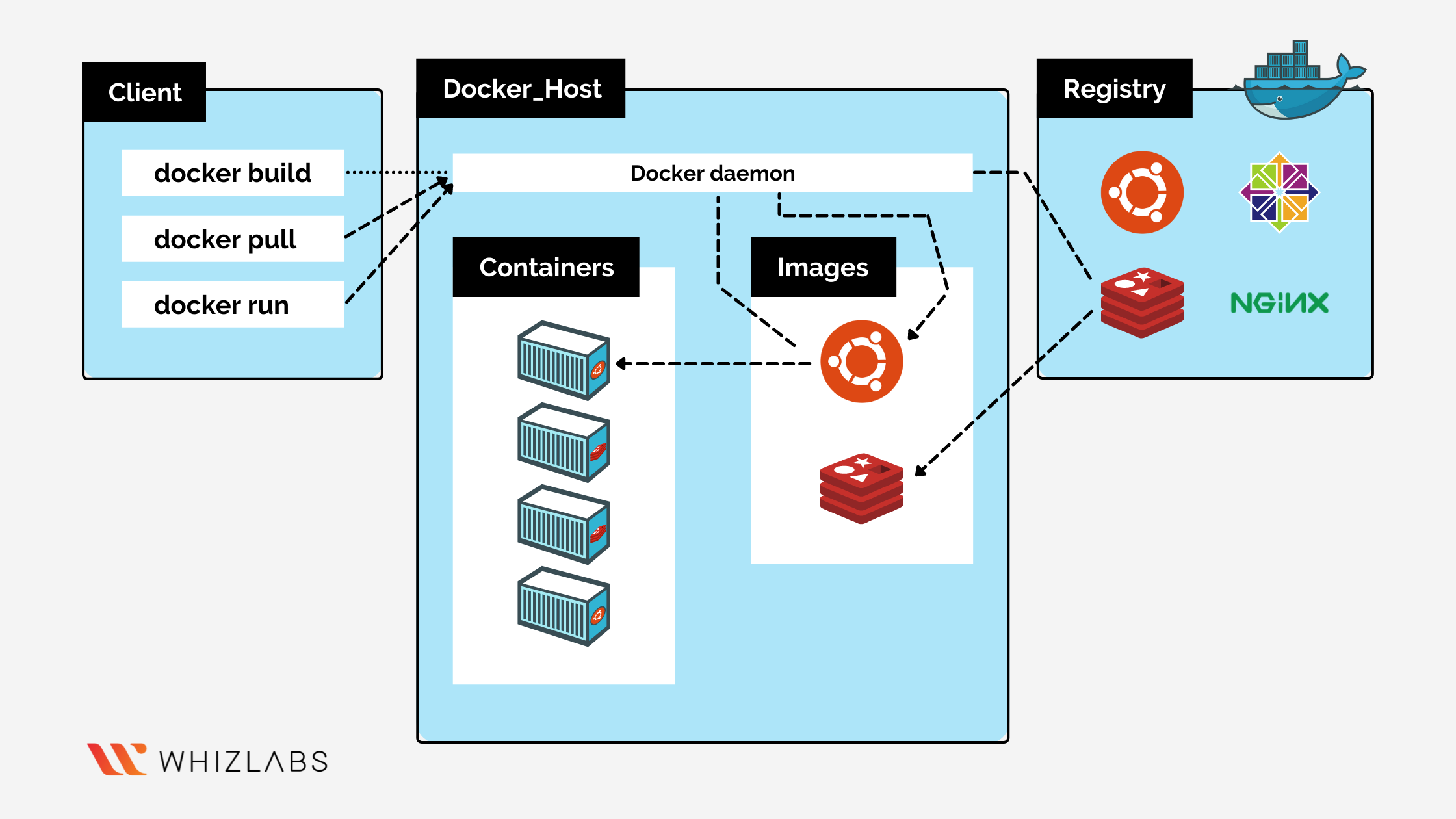
5. Explain
the Docker architecture.
Docker is based on client-server architecture.
Docker client talks to docker daemon (A long running program) via REST API over
a network interface or UNIX sockets. Docker client and daemon can run on the
same system or remote. Docker daemon is responsible for building, running and
distributing the containers.
Source: Docker Architecture
- Docker Daemon - responsible
to listen to API calls and manage docker objects. To manage Docker
services it can communicate with other docker daemon as well.
- Docker Client - is used to
communicate with docker daemon via REST APIs and can communicate with more
than one daemon.
- Docker Registries - Docker images
are stored in Docker registry. Docker Hub is a public
registry and a default location for docker images configured in docker.
- Docker Objects - When you are
using docker means you are going to use many things like images,
containers, volume, networks and many others, these are called docker
objects.
6. What is DTR (Docker Trusted Registry)?
If you are
using Docker Data Center (DDC), then Docker provides an enterprise grade image
storage solution called Docker Trusted Registry (DTR). DTR can be installed on
virtual private networks or on-premises so that you can store your images in a
secure way and behind your firewall. DTR also provides a User Interface that
can be accessed by authorized users to view and manage the repositories.
7. What are the common Docker objects?
With Docker
you use many things like Images, Containers, Registries, Services, Volumes etc.
These all are Docker objects.
8. Explain the Docker Images.
A Docker
Image is a read-only template with instructions that forms the basis
of a container. It's an order collection of file-system changes. Image is based
on another image with some customizations. For example, you can create an image
that is based on 'ubuntu' image but you can install other application
dependencies.
Images contain a set of run parameters (starting executable file) that will run
when the container starts.
9. Why Images are light weight, fast and small?
Docker
allows you to create your own image using a docker file with simple
instructions needed to create an image. Each instruction creates layers in
docker image. So when you make any changes in a docker file then only changed
layers are rebuilt, not all, this is the reason that docker images are fast,
small and light weight in comparison to other virtualization systems.
10. Describe Docker Containers?
Containers are
created from Images or you can say Container is a runnable instance of an
image. When you build your image and deploy the application with all the
dependencies then multiple containers can be instantiated. Each container is
isolated from one another and from the host machine as well. So A Docker
Container is defined by an image and other configurations provided
when you start or create it.
11. Explain the underlying technology of Docker.
Docker is developed in Go Language and has capability to use many Linux kernel features to deliver the functionality.
12. What is Dockerfile?
· Dockerfile is a
file that holds a set of instructions to create an image.
· Each
instruction of Dockerfile is responsible for creating a layer in the
image.
· When you rebuild the image, only changed layers are rebuilt.
13.Explain some quick facts about Docker.
Developers
are considering Docker as a good choice to deploy the application any time,
anywhere - OnPrem or Cloud. Let's know some facts about it.
- Docker was launched
by Solomon Hykes in 2013. Now Solomon Hykes is the CTO
and chief Architect of Docker.
- Docker allows us to
build, ship, run and orchestrate the applications in an isolated
environment.
- Docker is much faster
than starting a virtual machine, but virtual machines are not obsolete
yet.
- Docker Hub offers
free options to host public repositories by developers and paid options
for private repositories.
- Docker Desktop and
Docker Compose usage has reduced the local development environment setup
time that helps the developers to be productive.
14. What is the future of Docker?
- Docker
offers a quick way to build, develop, ship and orchestrate distributed
applications in isolated environments.
- Docker
is being used by many companies to make developer's processes faster.
Docker also provides automatic deployment management. So most companies
are adopting this containerized approach for their application development
and deployment.
- Docker
also provides integration with many hundreds of tools like Bitbucket, Jenkins, Kubernetes, Ansible, Amazon EC2
etc.
15. What is Docker Desktop?
Docker Desktop is an easy-to-install application for your Mac, Windows or Linux environment that enables you to build and share containerized applications and microservices. Docker Desktop includes the Docker daemon (dockerd), the Docker client (docker), Docker Compose, Docker Content Trust, Kubernetes, and Credential Helper.
16. What is Docker Compose?
Docker Compose is a tool that was developed to help define and share multi-container applications. With Compose, we can create a YAML file to define the services and with a single command, can spin everything up or tear it all down.
The big advantage of using Compose is you can define your application stack in a file, keep it at the root of your project repo (it’s now version controlled), and easily enable someone else to contribute to your project. Someone would only need to clone your repo and start the compose app.
Example:-
command:
docker run -d \
--network todo-app --network-alias mysql \
-v todo-mysql-data:/var/lib/mysql \
-e MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD=secret \
-e MYSQL_DATABASE=todos \
mysql:8.0
Compose:
services:
app:
image: node:18-alpine
command: sh -c "yarn install && yarn run dev"
ports:
- 3000:3000
working_dir: /app
volumes:
- ./:/app
environment:
MYSQL_HOST: mysql
MYSQL_USER: root
MYSQL_PASSWORD: secret
MYSQL_DB: todos
mysql:
image: mysql:8.0
volumes:
- todo-mysql-data:/var/lib/mysql
environment:
MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD: secret
MYSQL_DATABASE: todos
17. Create the Compose file?
- At the root of the app project, create a file named docker-compose.yml
- In the compose file, we’ll start off by defining the list of services (or containers) we want to run as part of our application.
- First, let’s define the service entry and the image for the container. We can pick any name for the service. The name will automatically become a network alias, which will be useful when defining our MySQL service.
- Typically, you will see the command close to the image definition, although there is no requirement on ordering. So, let’s go ahead and move that into our file.
- Let’s migrate the -p 3000:3000 part of the command by defining the ports for the service.
- Next, we’ll migrate both the working directory (-w /app) and the volume mapping (-v "$(pwd):/app") by using the working_dir and volumes definitions.
- Finally, we need to migrate the environment variable definitions using the environment key.
No comments:
Post a Comment