1. What is the concept of OOPs?
OOPs or
Object Oriented Programming systems have a certain set of principles or
concepts to write good programming logic. Basic OOPs concepts include:
- Abstraction
- Encapsulation
- Inheritance
- Polymorphism
2. What is
class, object and method?
Object Oriented programming
systems organize or manage the code by creating types in the form of classes.
A Class contains the code that represents a specific entity
and defines what an entity can do. For example, A BankAccount entity can be
organized by a class 'BankAccount'.
An entity has certain behavior, The code implements this behavior in the form
of operations or functions using Methods and Properties.
An Object is a block of memory that has been configured and
allocated according to the entity - which exists in the form of class.
3. What is
Abstraction?
Abstraction means
displaying only essential information and hiding the details. Data abstraction
refers to providing only essential information about the data to the outside
world, hiding the background details or implementation.
Consider a real life example
of a man driving a car. The man only knows that pressing the accelerators will
increase the speed of car or applying brakes will stop the car but he does not
know about how on pressing accelerator the speed is actually increasing, he
does not know about the inner mechanism of the car or the implementation of
accelerator, brakes etc in the car. This is what abstraction is.
4. Explain Encapsulation.
Encapsulation is concept that
binds together the data and functions that manipulate the data, and that keeps
both safe from outside interference and misuse.
Consider a real life example
of encapsulation, in a company there are different sections like the accounts
section, finance section, sales section etc. The finance section handles all
the financial transactions and keep records of all the data related to finance.
Similarly the sales section handles all the sales related activities and keep
records of all the sales. Now there may arise a situation when for some reason
an official from finance section needs all the data about sales in a particular
month. In this case, he is not allowed to directly access the data of sales
section. He will first have to contact some other officer in the sales section
and then request him to give the particular data. This is what encapsulation
is. Here the data of sales section and the employees that can manipulate them
are wrapped under a single name “sales section”.
5. Explain Inheritance in detail.
The capability of a class to
derive properties and characteristics from another class is called Inheritance.
Inheritance is one of the most important features of Object-Oriented
Programming.
Inheritance is a feature or a
process in which, new classes are created from the existing classes. The new
class created is called “derived class” or “child class” and the existing class
is known as the “base class” or “parent class”. The derived class now is said
to be inherited from the base class.
When we say derived class
inherits the base class, it means, the derived class inherits all the
properties of the base class, without changing the properties of base class and
may add new features to its own. These new features in the derived class will
not affect the base class. The derived class is the specialized class for the
base class.
- Sub
Class:
The class that inherits properties from another class is called Subclass
or Derived Class.
- Super
Class:
The class whose properties are inherited by a subclass is called Base Class
or Superclass.
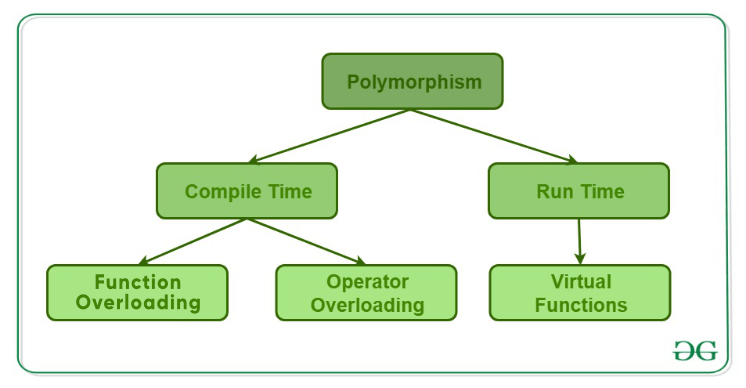
6. Explain Polymorphism.
The word “polymorphism” means
having many forms. In simple words, we can define polymorphism as the ability
of a message to be displayed in more than one form. A real-life example of
polymorphism is a person who at the same time can have different
characteristics. Like a man at the same time is a father, a husband and an
employee. So the same person exhibits different behavior in different
situations. This is called polymorphism.
polymorphism is mainly
divided into two types:
- Compile-time
Polymorphism
- Runtime
Polymorphism
Compile-time polymorphism: This type of polymorphism is
achieved by function overloading or operator overloading.
Function
Overloading: When there are multiple functions with the same name but different
parameters, then the functions are said to be overloaded. Functions can be
overloaded by changing the number of arguments or/and changing the type of
arguments.
Operator
Overloading: C++ also provides the option to overload operators. For
example, we can make use of the addition operator (+) for string class to
concatenate two strings. We know that the task of this operator is to add two
operands. So a single operator ‘+’, when placed between integer operands, adds
them and when placed between string operands, concatenates them.
Runtime
polymorphism: This type of polymorphism is achieved by Function
Overriding.
Function
overriding occurs when a derived class has a definition for one of
the member functions of the base class. That base function is said to be
overridden.
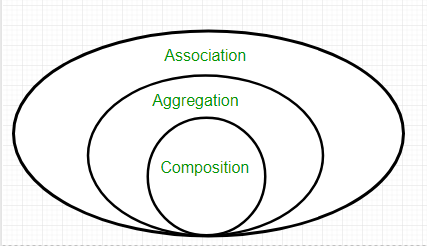
7. What is Association?
Association is a relation
between two separate classes which establishes through their Objects.
Association can be one-to-one, one-to-many, many-to-one, many-to-many. In
Object-Oriented programming, an Object communicates to another object to use
functionality and services provided by that object. Composition and Aggregation are
the two forms of association.
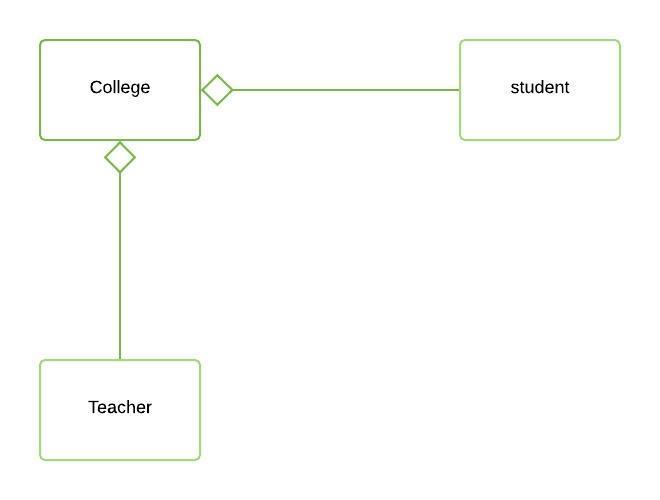
8. What is Aggregation?
It is a special form of
Association where: It represents Has-A’s relationship.
It is a unidirectional
association i.e. a one-way relationship.
For example, a department can
have students but vice versa is not possible and thus unidirectional in
nature.
In Aggregation, both the
entries can survive individually which means ending one entity will not affect
the other entity.
Aggregation is a weak
Association.
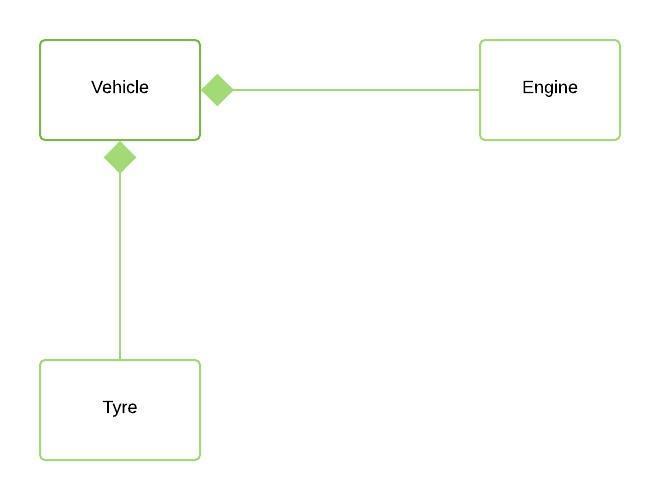
9. What is composition?
Composition is a restricted
form of Aggregation in which two entities are highly dependent on each other.
It represents part-of
relationship.
In composition, both entities
are dependent on each other. When there is a composition between two entities,
the composed object cannot exist without the other entity.
Composition is a strong
Association
10. What is
Cohesion?
Cohesion is the
Object-Oriented principle most closely associated with making sure that a class
is designed with a single, well-focused purpose. In object-oriented design,
cohesion refers to how a single class is designed.
The advantage of high
cohesion is that such classes are much easier to maintain (and less frequently
changed) than classes with low cohesion. Another benefit of high cohesion is
that classes with a well-focused purpose tend to be more reusable than other
classes.
Example: Suppose we
have a class that multiplies two numbers, but the same class creates a pop-up
window displaying the result. This is an example of a low cohesive class
because the window and the multiplication operation don’t have much in common.
To make it high cohesive, we would have to create a class Display and a class
Multiply. The Display will call Multiply’s method to get the result and display
it. This way to develop a high cohesive solution.
Explanation: In the
above image, we can see that in low cohesion only one class is responsible to
execute lots of jobs that are not in common which reduces the chance of
reusability and maintenance. But in high cohesion, there is a separate class
for all the jobs to execute a specific job, which results in better usability
and maintenance.
Difference
between high cohesion and low cohesion:
High cohesion is when you
have a class that does a well-defined job. Low cohesion is when a class does a
lot of jobs that don’t have much in common.
High cohesion gives us
better-maintaining facility and Low cohesion results in monolithic classes that
are difficult to maintain, understand and reduce re-usability
11. What is
Coupling?
Coupling is a degree of measure that indicates how closely connected two classes are. If the coupling is high then changes in one class affects the code in other classes and makes code difficult to maintain and change. Applications with low coupling ensure better code maintainability and any code changes can be easily implemented without affecting other classes or systems. A good application design must have High Cohesion and Low Coupling.

No comments:
Post a Comment